

The colour circle, first devised by Newton, is still widely used for purposes of colour design and is also useful when the qualitative behaviour of mixing beams of light is considered.
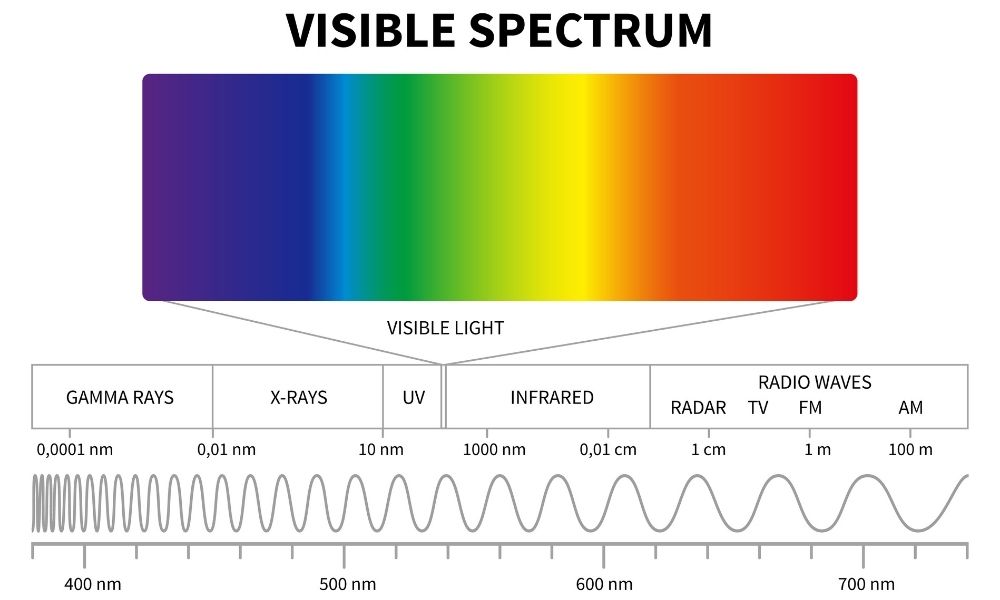
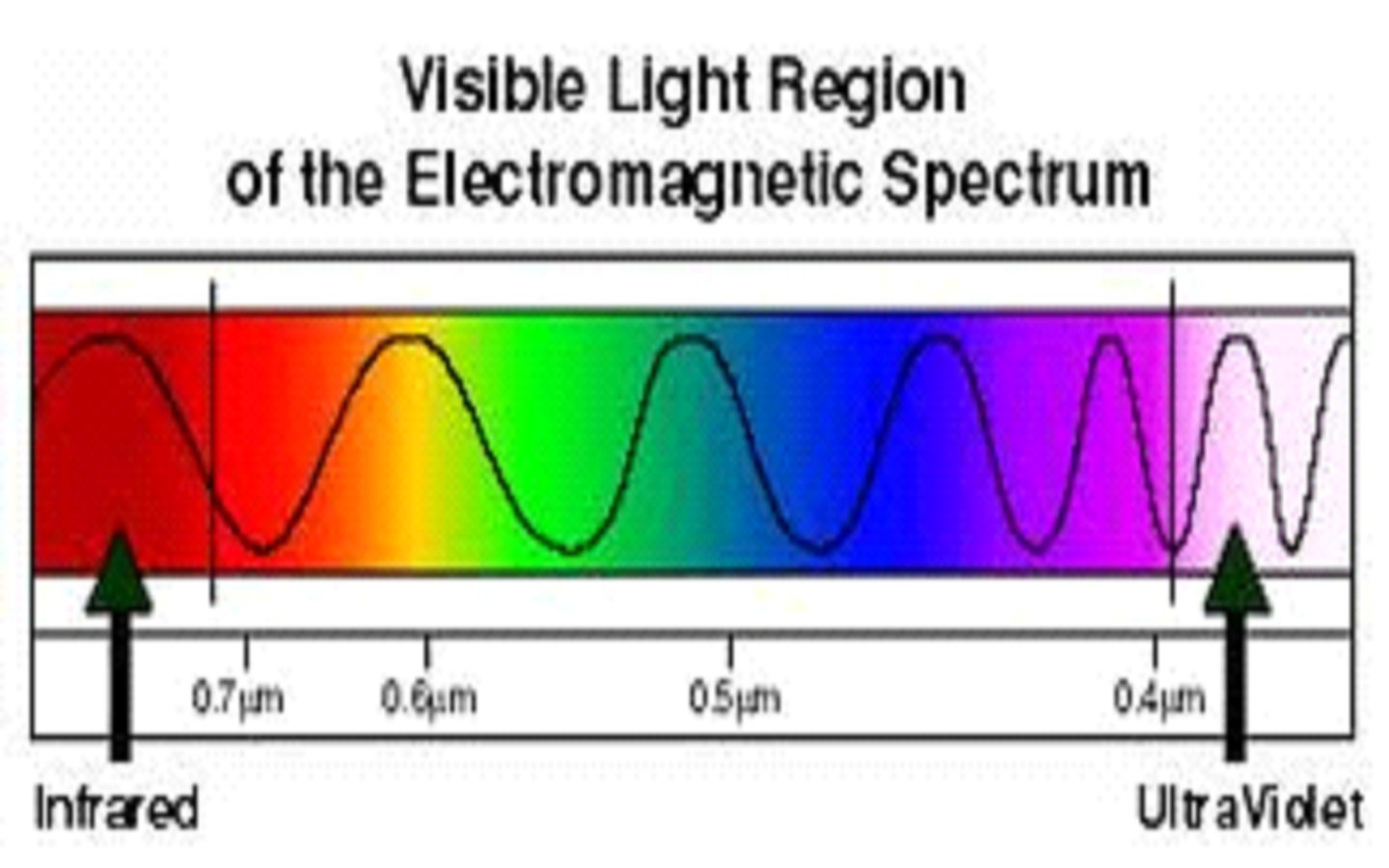
When this frequency falls in the range of the visible spectrum, the colour perception produced is that of a saturated hue.Īdditive mixing occurs when beams of light are combined. Radiation of a single frequency is called monochromatic. Just beyond the red end of the spectrum are the longer wave infrared radiation rays (which can be felt as heat), microwaves, and radio waves. (The limits of the visible spectrum are not sharply defined but vary among individuals there is some extended visibility for high-intensity light.) At shorter wavelengths the electromagnetic spectrum extends to the ultraviolet radiation region and continues through X-rays, gamma rays, and cosmic rays. Wavelengths of light range from about 400 nm at the violet end of the spectrum to 700 nm at the red end ( see table). Light is not the only type of electromagnetic radiation-it is, in fact, only a small segment of the total electromagnetic spectrum-but it is the one form the eye can perceive.
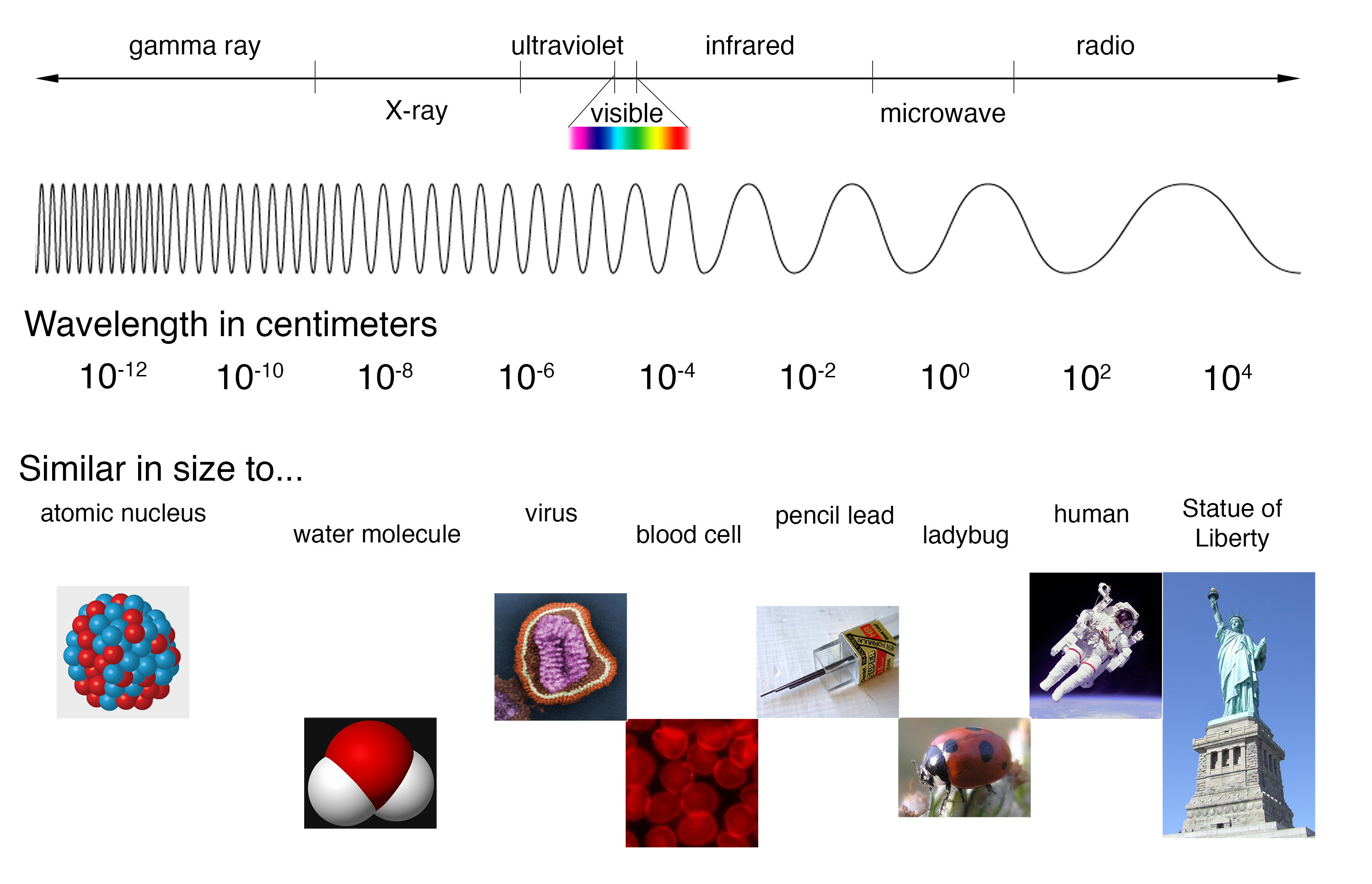
The energy of a photon is often expressed in units of electron volts (1 eV = 1.602 × 10 −12 erg) it is directly proportional to frequency and inversely proportional to wavelength. The name photon, used for the smallest quantity of light of any given wavelength, is meant to encompass this duality, including both the wave and particle characteristics inherent in wave mechanics and quantum mechanics. The energy of a light beam can be compared to that possessed by a small particle moving at the velocity of light, except that no particle having a rest mass could move at such a velocity. Wavelength is the distance between corresponding points of two consecutive waves and is often expressed in units of metres-for instance, nanometres (1 nm = 10 −9 metre). Frequency, which is the number of waves passing a fixed point in space in a unit of time, is commonly expressed in units of hertz (1 Hz = 1 cycle per second). Any given beam of light has specific values of frequency, wavelength, and energy associated with it. It can be thought of as a stream of minute energy packets radiated at varying frequencies in a wave motion. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, light has properties in common with both waves and particles. To understand colour, therefore, it is necessary to know something about light. Newton demonstrated that colour is a quality of light. Uncover through science what makes black color the way it is and how researchers are developing the real pure version of black See all videos for this article SpaceNext50 Britannica presents SpaceNext50, From the race to the Moon to space stewardship, we explore a wide range of subjects that feed our curiosity about space!.Learn about the major environmental problems facing our planet and what can be done about them! Saving Earth Britannica Presents Earth’s To-Do List for the 21st Century.Britannica Beyond We’ve created a new place where questions are at the center of learning.100 Women Britannica celebrates the centennial of the Nineteenth Amendment, highlighting suffragists and history-making politicians.
Light spectrum how to#
COVID-19 Portal While this global health crisis continues to evolve, it can be useful to look to past pandemics to better understand how to respond today.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
